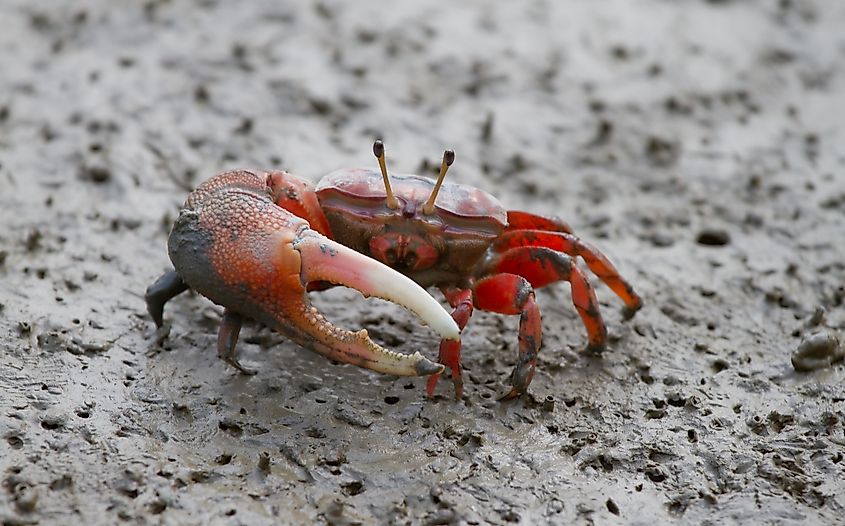
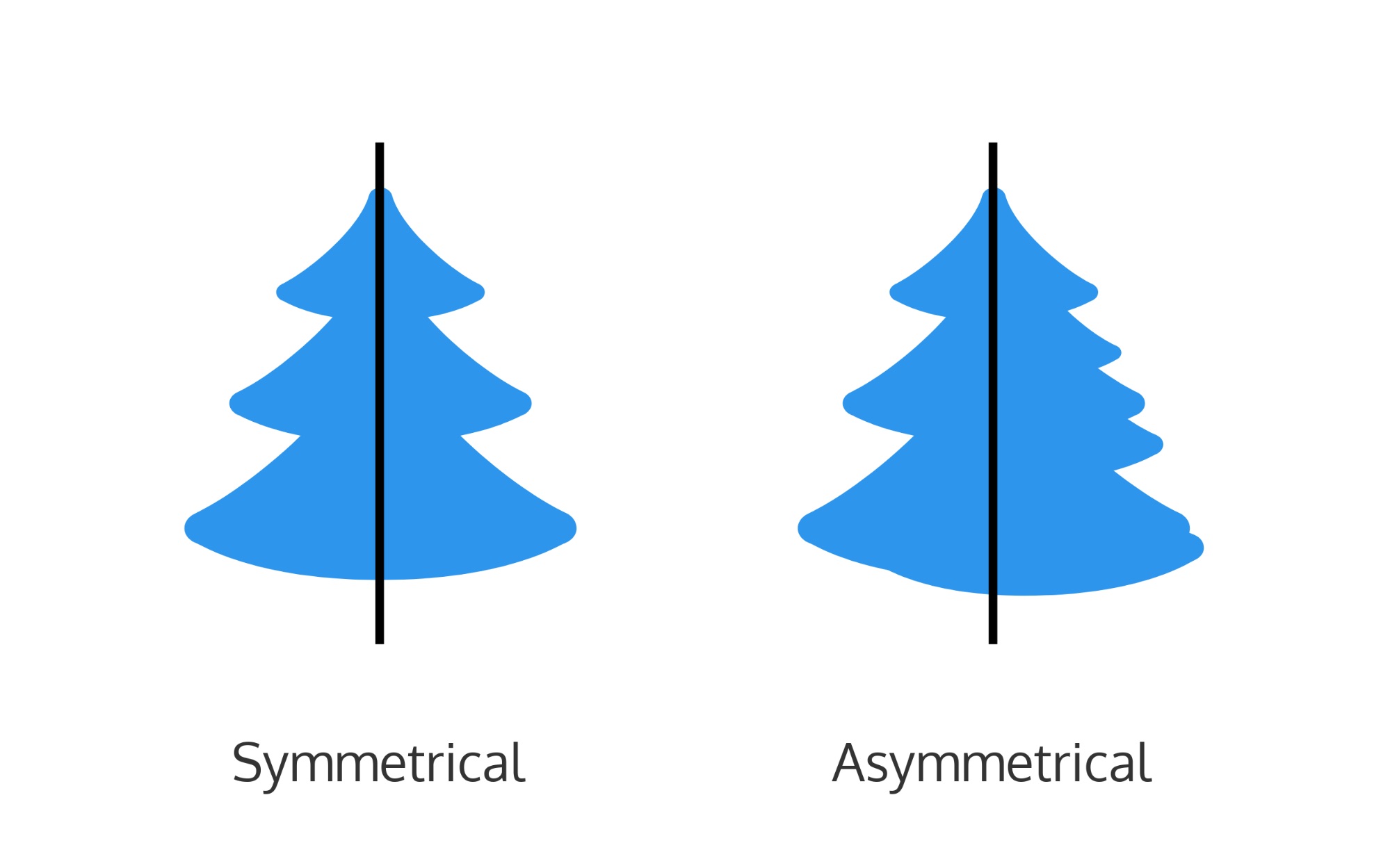
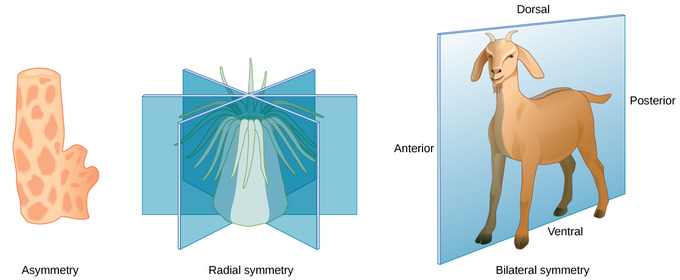
The mechanisms orchestrating this process are extremely complex.The emergence of symmetry cannot be fully understood without considering the emergence of asymmetry as well.
However, roles for asymmetric division in other more dynamic morphogenetic processes, such as cell migration, have not previously been described.Haeckel's biogenetic law, or the recapitulation theory remains a controversial subject to this day.For instance, lopsided flatfish that lie on one side of their body and have both eyes on the other;
Take, for example, the human brain, one of the.In recent decades, polarity formation in asymmetric cell division has been extensively explored using caenorhabditis elegans embryos as a biological model system.
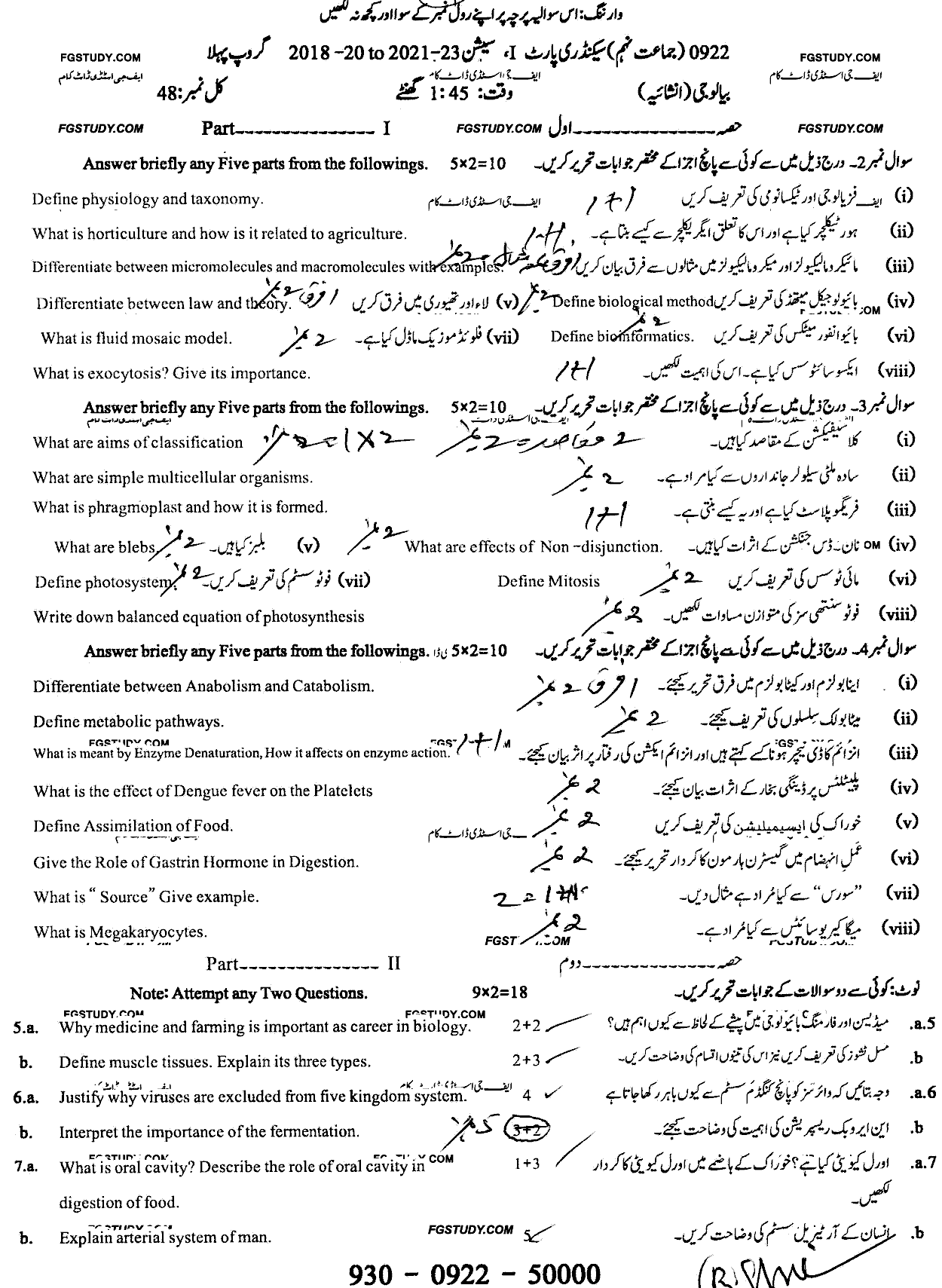
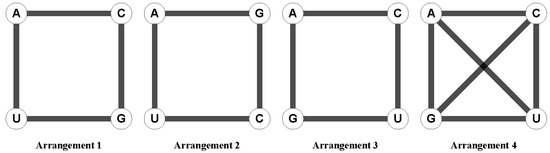
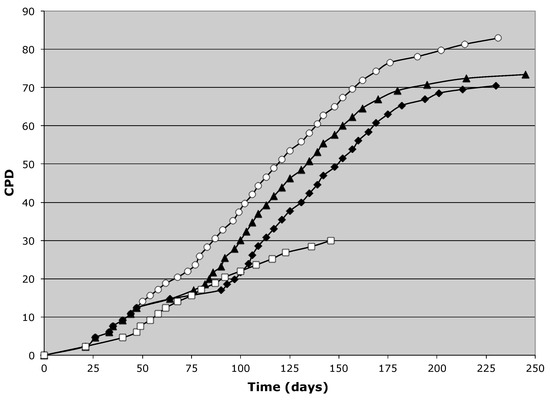
In mitosis, this axis is used for spindle orientation.The asymmetric division of stem or progenitor cells generates daughters with distinct fates and regulates cell diversity during tissue morphogenesis.Elegans, the symmetry is disrupted at the pole where the posterior end is formed after sperm entry.concurrently, the acto‐myosin network in the cell cortex begins contracting from the.
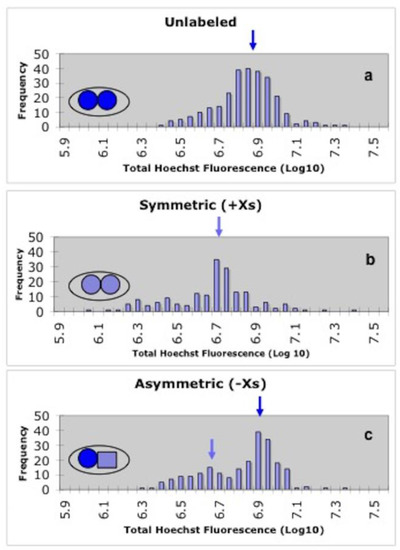
A key principle of acd is the establishment of distinct sibling cell fates by mechanisms linked to mitosis.During asymmetric division, proteins, organelles, and even rna are distributed unequally between the two daughter cells, determining their distinct cell fates.
Last update images today Define Asymmetrical In Biology
 Wolvaardt: SA 'pretty Close' To Nailing Best XI For T20 World Cup
Wolvaardt: SA 'pretty Close' To Nailing Best XI For T20 World Cup
It is often said that the early 2010s represented the best of the A-League. Surging crowds, big names, and genuine mainstream interest embuing the competition with an aura that something special was afoot. The real "Peak A-League," if you will.
Alas, that's not the early 2010s throwback the league is set to provide for the foreseeable future. Instead, welcome to that other, not-so-welcome early 2010s throwback; the A-League's very own Age of Austerity.
Its dawn arrived on Wednesday, as league administrators the Australian Professional Leagues (APL), admitted that it spent "spent too much money," in pursuit of an "overly ambitious" agenda, and confirmed grants distributed to clubs for the 2024-25 season had been slashed to just $530k, with clubs receiving approximately $1.5 million less than in the season prior.
At one stage in the competition's history, clubs could rely on these payments from the league to cover the entirety of the A-League Men's salary cap. Now, next season's distribution will be around $3m less than the highs it reached pre-unbundling from Football Australia. Clubs will need to find upwards of $2m of their own funding to meet base requirements of the competitions' salary caps: a minimum of $2.25m in the A-League Men, and a minimum $500,000 in the A-League Women. And that's before one even gets to paying for coaches, support and backroom staff, facilities, ground hire, and everything else that goes into a club.
Yet, while Wednesday's confirmation of this reduction will in the future provide something of a neat and clear jumping-off point in the historical record, this era of austerity, really, was probably already underway.
Many clubs spent well over the salary cap in previous seasons, for instance, with the various exceptions and rules devoted to marquee players, designated players, loyalty players, and so on, ensuring the cap had more holes than Swiss cheese. However, the COVID-19 pandemic largely forced A-League clubs to recalibrate how they approached squad building, forcing a demographic change. And it's those already existing trends that will likely be built upon in the wake of these cuts: The days of numerous marquee, designated, and loyalty players -- all of whom came at a cost greater than their actual salary cap hit -- are long gone. Clubs have already been forced to get younger, get cheaper, and rely less on foreign talent, and this will continue.
The APL, meanwhile, shed half its workforce earlier in the year and shuttered its ill-fated digital arm KEEPUP. "Right-sizing," as it was put in Wednesday's press release -- language that probably appeals only to a person who spends far too much time on LinkedIn.
Instead, Wednesday perhaps more likely represented rock bottom. Or to be more accurate, what the APL hopes will be rock bottom. In making the various cuts to its workforce and operations, and reducing distributions to clubs, the organisation is seeking to break even in the coming year -- consolidating ahead of a new TV deal that A-League commissioner Nick Garcia believes will provide much-needed relief, given the three years of growth in the A-League's key metrics.
Most of the architects of the APL's ill-fated strategy have departed (invariably landing a lot more softly than the rank and file made redundant). Inaugural chair Paul Lederer stepped off the APL board in December 2023 and ended his tenure as chair of Western Sydney Wanderers last month. Sydney FC's Scott Barlow exited the APL board in June, and Anthony Di Pietro stood down amid the Grand Final sale debacle. Former chief executive Danny Townsend departed last October, and ex-chief commercial officer Ant Hearne left a month later. The most influential figure remaining from the unbundling process is City Football Group figure Simon Pearce, whom APL chairperson Stephen Conroy declined to speak about when asked if he would remain on the board on Wednesday; instead, Conroy painted a less specific, broader picture of new-look leadership following elections in September.
And given the tide of reports that austerity was coming, and how the league got here, few paying attention are likely shocked by the cuts. Garcia and Conroy were adamant there had been communication with all A-League clubs throughout the process, and ESPN has spoken to multiple figures who were anticipating a reduced figure -- with at least one club making contingencies for a scenario wherein there was no grant at all. Thus, while the league getting into this state is extremely shocking, Wednesday's news, in a vacuum, probably wasn't.
Across a near hour-long call with media, Conroy and Garcia were quick to press a view that the impacts of a reduction in club grants didn't have to be detrimental to the on-field product. Central Coast Mariners, it was observed, were closest to the salary floor in the A-League Men last season but still achieved a historic treble of a premiership, an AFC Cup, and a second straight title. They also indicated that most -- if not all -- the clubs' existing commitments meant they had already met the salary floor for the coming season, and that none had indicated they would experience any sort of existential peril as a result of the cuts.
And the Mariners' blueprint, as well as Wellington Phoenix's, demonstrates that young squads put together on a budget needn't portend disastrous results or passionless football. The degree of difficulty is much greater than if one were working with a blank cheque, of course, and each club's circumstances mean they need to find a bespoke approach rather than simply copying others -- the Nix's model wouldn't work for Melbourne Victory's circumstances, and so on -- but it is possible. And in a time of austerity, when getting fans in the stands week in and week out is so important, club boards should have already been applying pressure to football departments not only to put in place clear strategies around the development and sale of players to bolster bottom lines, but also play a brand of football, even with perceived "lesser" talent, that excites and resonates with supporters. Not just as a preference, but as a need. Indeed, it's a demand that should not even require austerity.
A concern, however, comes with the inevitability that the gap left by the reduction in grants, unable to be completely covered by new sources of revenue and/or owners being unwilling to further dip into their own pockets, will come in the form of savings. Football is hardly alone in experiencing this, of course; most people have experienced, or know someone who has experienced, a redundancy in the current economy. And several clubs have already begun shrinking both on- and off-field workforces --- the blunders of others leaving them in the lurch amid a cost-of-living crisis. On a broader level, however, a risk is that club owners and boards, driven by a short-termism that has haunted Australian football, find savings in the very tools areas that offer promises of long-term sustainability; cutting back on the academies that produce players who can be sold, women's programs that have only scratched the surface of their commercial potential, and so on.
When asked what the cuts in grants would mean for the A-League Women, for instance, Garcia pointed to the provisos in club participation agreements requiring a women's team, and the collective bargaining agreement with the players' union that guaranteed minimum remuneration and conditions. ESPN has since approached the APL for comment on whether Auckland FC and Macarthur FC will still enter women's teams in 2025-26 season, as planned.
But it's here where we get to the tricky bit. What's next?
On the A-League Women's front, the APL is on record wanting the competition to become a destination league on a global level, recognised as Asia's best. To do that, though, it needs to invest, especially in full-time professionalism. Players, the majority of whom still can't survive on a football salary alone, have been calling for it for years, agitating in recent months for the APL to lay out an actual vision for how they're going to reach this point. But on Wednesday, Garcia said this pathway was something to be mapped out in the coming months, as well as several other roadmaps for the league's future, now that the funding cuts were in place.
The same goes for the A-League Men's shift towards developing and selling players. It's long overdue, and regulatory changes have been flagged, but, at the same time, there's still no youth competition and the league is on the verge of reducing the number of games it will play next season. Something's got to give.
And therein lies the rub. The very future of the A-League rests, we're told, upon a leaner, "football first" approach. What that exactly looks like, though, we don't know. Perhaps the APL doesn't even completely know yet. But whatever it is, it needs to become apparent fast. Because fans, players, and everyone else who still cares about the A-League, need a reason to hopeful for the competition's future.